Child abuse is not just physical injuries that happen at one point in time. Child abuse causes problems for everyone in society. Child abuse hurts children during childhood and affects normal development into adulthood (Stoltenborgh, Van IJzendoorn, Euser & Bakermans-Kranenburg, 2011). Child abuse both physical and sexual is associated with decreased educational attainment later in life (Broden, Horwood, & Fergusson, 2007). Furthermore, child abuse has been associated with an increased likelihood of developing psychiatric disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and major depressive disorder (Fergusson, Horwood, & Lynskey, 1996). The problem that child abuse causes are not limited to just the person experiencing the abuse. According to Stoltenborgh, Van IJzendoorn, Euser, and Bakermans-Kranenburg (2011), the families are also greatly affected including the not abusing parent or other non-abuse children. The negative effects of child abuse are accepted among the psychiatric community including counselors, psychologists and physicians (Stoltenborgh, Van IJzendoorn, Euser & Bakermans-Kranenburg, 2011).
Difficulties Surrounding Child abuse
Getting accurate numbers on child abuse is difficult because many people are afraid to report child abuse or look only at one form of child abuse such as neglect or physical abuse (Stoltenborgh et al., 2011). Furthermore, child abuse is often under reported because people do not want to interfere with other people's lives and multiple children living in one home is considered one case (Childhelp, 2011). As a result of the difficulties in reporting or understanding child abuse, defining child abuse is just as difficult. According to the Hammond (2011), from the Center for Disease control, the definition of child abuse or maltreatment is,
"any act or series of acts of commission or omission by a parent or caregiver that results in harm, potential harm, or threat of harm to a child. Much of the child maltreatment field divides acts of commission into three broad categories physical, sexual, or emotional abuse. Acts of omission are often referred to as child neglect and divided into two categories failure to provide for a child’s basic needs and failure to protect a child."
With regard to child abuse, the broadest definition possible should be used because of the potential harm associated with child abuse.
An additional difficulty associated with child abuse is the conceptualization. The conceptualization is something that must be clearly understood and defined within the community. As a result of confusion over child abuse, children from a lower socioeconomic status have an increased likelihood of being victims of child abuse (Stouthamer-Loeber, Wei, Homish, & Loeber, 2002). Items that are associated with a lower socioeconomic status are items such as lower income, less education, and/or single parent. According to Stouthamer-Loeber et al., (2002), people who are taking care of children that are poorly educated, have less communication with the children, and when the child was not living with both biological parents there was an increased likelihood of maltreatment. The low socioeconomic status is linked with child abuse or maltreatment, but it is unclear whether the low socioeconomic status is causing the child abuse or if child abuse is part of low socioeconomic status. This does not mean that children do not get abuse that are from a family with high socioeconomic status, but items such as low socioeconomic status, less communication, and poorly educated caregivers are risk factors that provide a greater chance of child abuse happening.
Furthermore, child abuse is a problem that affects everyone because it cause problems later in life for the individual abuse that could influence thing such as unstable relationships or negative effects on the relationship (Larsen, Sandberg, Harper,& Bean, 2011).
Who is the perpetrator?
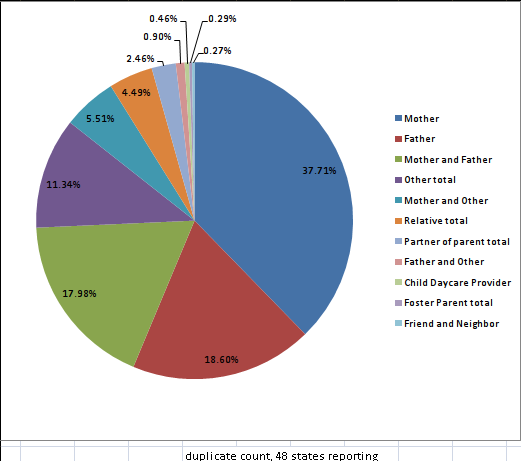
The perpetrator of child abuse can be a stranger, mother, father, mother and father, or relatives. According to the U.S. Department of health and human services (2011), mothers, fathers, and mothers and fathers account for 72.29% of reported child abuse cases. The percentage of parents engaging in child abuse indicates that children are at the most risk when they are at home dispelling the myth that child abuse is most likely experienced because of a stranger. In relation to the perpetrators, the type of abuse is also important. According to U.S. Department of health and human services (2009), neglect was the most common form of child abuse (66.7%), and physical abuse being 44.8%. Child neglect being the most prevalent form of child abuse is the act of not meeting the needs of the child (Mennen, Kim, Sang, & Tickett, 2010).
Child abuse is a pervasive act that hinders a child to develop in to a healthy child. The act of hurting a child whether it is omission or commission it is something a child cannot readily defend against, and as such individuals need to advocate for child that have been abuse, educate other so children do not become victims, and most importantly stop those who are abusing.